背景
上周末(2019年10月20日)参加了 TUG 华南区在 Shopee 举办的第三期线下技术沙龙活动,以“不同业务场景下的数据库技术选型思路”来展开分享和探讨的。
其中刘春辉和洪超老师分享了 Shopee 的数据库技术选型思路,在分享中,大家对全局唯一 ID 还挺有疑惑的,那我们今天就来看看 TiDB 中全局唯一 ID 是怎么实现的吧。
文章最后附上活动信息
PD
Placement Driver (简称 PD) 是整个集群的管理模块,其主要工作有三个:一是存储集群的元信息(某个 Key 存储在哪个 TiKV 节点);二是对 TiKV 集群进行调度和负载均衡(如数据的迁移、Raft group leader 的迁移等);三是分配全局唯一且递增的事务 ID。
PD 的命名,来源于 Google Spanner - Spanner:Google's Globally-Distributed Database [译文]。 Spanner 论文
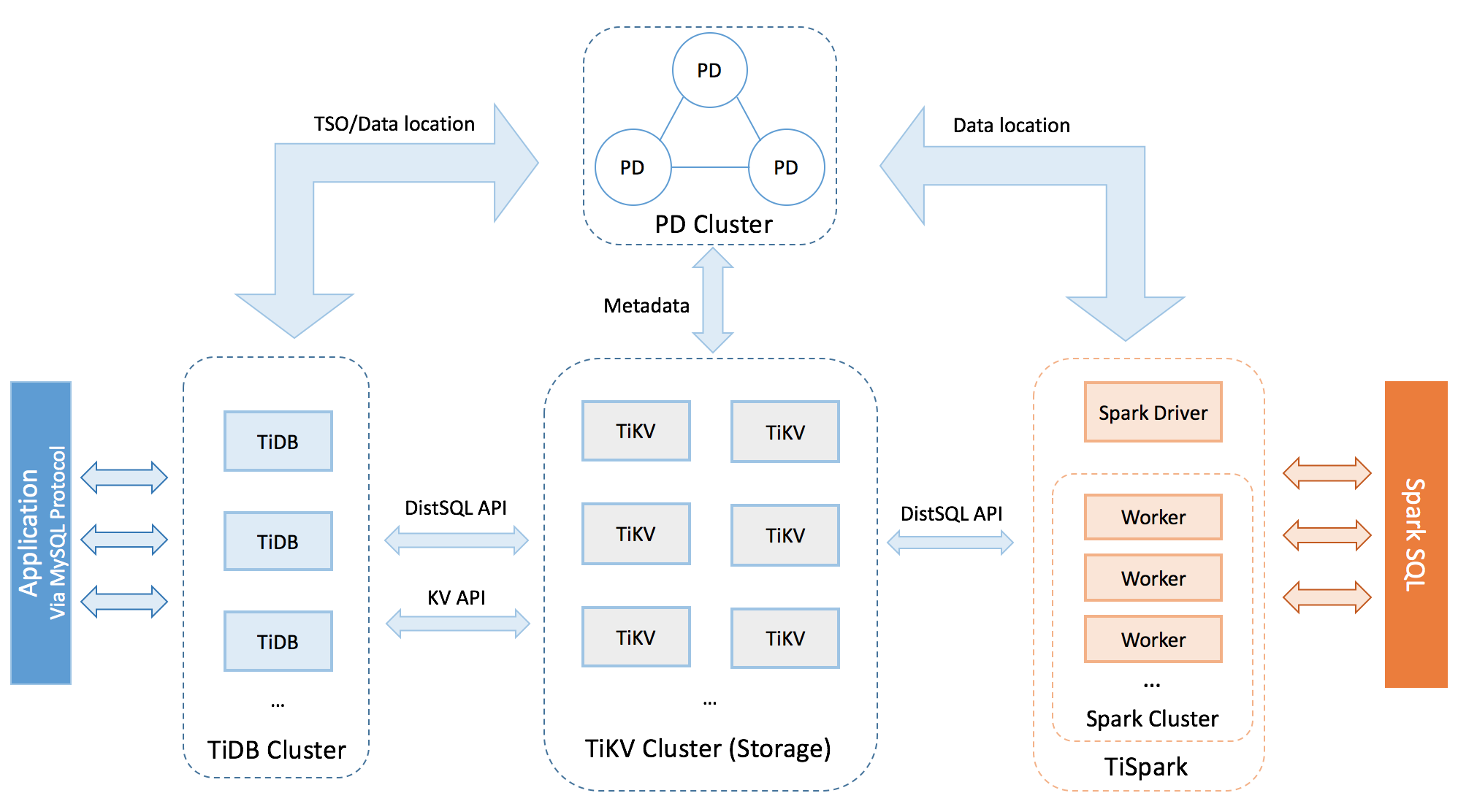
TiDB 架构图(重点看 PD 跟其他的组件的关系):
分布式 ID
单调递增的 id 能干的事可多了,可以用来实现数据库的 MVCC,进而实现 ACID 事务,检测冲突什么的。在分布式系统中尤其重要,这个领域其实说白了就是不停在和不确定的 wall clock 作斗争… 如何用更弱的约束达到更强的一致性,我觉得单调递增的唯一 id 生成器是一个利器
1
2
3
4
|
作者:Ed Huang
链接:https://www.zhihu.com/question/52823076/answer/132331104
来源:知乎
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
|
业界一般的技术方案
- 单机数据库 auto_increment;
- 单点批量 ID 生成服务;
- Redis INCR INCRBY;
- uuid/guid;
- 取当前毫秒数;
- Snowflake
- 利用 zookeeper 生成唯一 ID
- MongoDB 的 ObjectId
扩展技术方案
- 百度 UidGenerator
UidGenerator 是 Java 实现的, 基于 Snowflake 算法的唯一 ID 生成器。UidGenerator 以组件形式工作在应用项目中, 支持自定义 workerId 位数和初始化策略, 从而适用于 docker 等虚拟化环境下实例自动重启、漂移等场景。 在实现上, UidGenerator 通过借用未来时间来解决 sequence 天然存在的并发限制; 采用 RingBuffer 来缓存已生成的 UID, 并行化 UID 的生产和消费, 同时对 CacheLine 补齐,避免了由 RingBuffer 带来的硬件级「伪共享」问题. 最终单机 QPS 可达 600 万。
- 美团 Leaf
Leaf 提供两种生成的 ID 的方式(号段模式和 snowflake 模式),你可以同时开启两种方式,也可以指定开启某种方式(默认两种方式为关闭状态)。
在4C8G VM基础上,通过公司RPC方式调用,QPS压测结果近5w/s,TP999 1ms。
PD 分配 ID 的场景
- 生成 Cluster ID
- 防止用户多个集群配错了,或者重新部署时数据没清干净
- 生成唯一 ID
- RegionID,StoreID,PeerID,etc.
我们接下来就来看看他们的源码实现吧。
生成 Cluster ID
pd 在 startServer() 的时候调用 initClusterID() 可以初始化 Cluster ID。
首先会从 etcd 中读取,取不到,则重新生成。
生成 Cluster ID 的算法:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
// Generate a random cluster ID.
ts := uint64(time.Now().Unix())
clusterID := (ts << 32) + uint64(rand.Uint32())
value := typeutil.Uint64ToBytes(clusterID)
// Multiple PDs may try to init the cluster ID at the same time.
// Only one PD can commit this transaction, then other PDs can get
// the committed cluster ID.
resp, err := c.Txn(ctx).
If(clientv3.Compare(clientv3.CreateRevision(key), "=", 0)).
Then(clientv3.OpPut(key, string(value))).
Else(clientv3.OpGet(key)).
Commit()
// Txn commits ok, return the generated cluster ID.
if resp.Succeeded {
return clusterID, nil
}
|
解析分配唯一 ID 的过程
1. pd service 的定义
首先,我们可以通过 kvproto/proto/pdpb.proto 来查看 pd 所定义的服务有哪些。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
|
service PD {
...
rpc AllocID(AllocIDRequest) returns (AllocIDResponse) {}
...
}
message AllocIDRequest {
RequestHeader header = 1;
}
message AllocIDResponse {
ResponseHeader header = 1;
uint64 id = 2;
}
message RequestHeader {
// cluster_id is the ID of the cluster which be sent to.
uint64 cluster_id = 1;
}
message ResponseHeader {
// cluster_id is the ID of the cluster which sent the response.
uint64 cluster_id = 1;
Error error = 2;
}
enum ErrorType {
OK = 0;
UNKNOWN = 1;
NOT_BOOTSTRAPPED = 2;
STORE_TOMBSTONE = 3;
ALREADY_BOOTSTRAPPED = 4;
INCOMPATIBLE_VERSION = 5;
REGION_NOT_FOUND = 6;
}
message Error {
ErrorType type = 1;
string message = 2;
}
|
如果你对 protobuf 还不太了解的话,可以点击前往,咱们这里就不做详细阐述了。
2. AllocID service 的实现。
怎么查找到 AllocID 的实现呢?
检索:AllocID,然后结合我们的 pdpb.proto service 定义,我们就可以对照出结果。
实现代码在:grpc_service.go#L141。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
// AllocID implements gRPC PDServer.
func (s *Server) AllocID(ctx context.Context, request *pdpb.AllocIDRequest) (*pdpb.AllocIDResponse, error) {
// 1. 校验请求数据,这里是在 pdpb.proto 中封装成 RequestHeader
if err := s.validateRequest(request.GetHeader()); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
// 2. 我们用一个 idAllocator 来分配 ID
// We can use an allocator for all types ID allocation.
id, err := s.idAllocator.Alloc()
if err != nil {
return nil, status.Errorf(codes.Unknown, err.Error())
}
// 3. 返回请求时的 header 和生成的 ID
return &pdpb.AllocIDResponse{
Header: s.header(),
Id: id,
}, nil
}
|
3. 初始化 idAllocator
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
// Server is the pd server.
type Server struct {
// Server services.
// for id allocator, we can use one allocator for
// store, region and peer, because we just need
// a unique ID.
idAllocator *id.AllocatorImpl
}
func (s *Server) startServer() error {
}
|
idAllocator 是在 server.Run 的时候,调用 startServer 时初始化的。
1
2
3
|
func (s *Server) startServer() error {
s.idAllocator = id.NewAllocatorImpl(s.client, s.rootPath, s.member.MemberValue())
}
|
4. 源码阅读 AllocatorImpl
我们根据上一步,可以看到在 pd/server/id/id.go 声明了一个 interface:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
// Allocator is the allocator to generate unique ID.
type Allocator interface {
Alloc() (uint64, error)
}
// 步长 1000
const allocStep = uint64(1000)
// AllocatorImpl 是对 Allocator 的实现,用于分配 ID
// AllocatorImpl is used to allocate ID.
type AllocatorImpl struct {
mu sync.Mutex
base uint64
end uint64
// etcd client
client *clientv3.Client
rootPath string
member string
}
// NewAllocatorImpl creates a new IDAllocator.
func NewAllocatorImpl(client *clientv3.Client, rootPath string, member string) *AllocatorImpl {
return &AllocatorImpl{client: client, rootPath: rootPath, member: member}
}
|
4. Alloc
基本逻辑是:
在 generate() 时会从 etcd 中载入之前持久化的已经发过的 id 作为起点。然后执行一次持久化,将起始 id + allocStep 保存下来。 [id, id + allocStep) 的区间就是缓存。客户端请求时,下发的 id 都是从这个缓存中取的。所以,对于高并发的应用,配置一个大的缓存区间可以获取更高的性能。比如将 allocStep 设为 5000,平均发出 5000 个号才需要持久化一次。
如果出现 pd 服务中断的话,重启启动时会从 etcd 中重新载入配置。(etcd 为高可用)
Alloc ID 的代码,加上注释 66 行。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
|
// Alloc returns a new id.
func (alloc *AllocatorImpl) Alloc() (uint64, error) {
// 给分配增加锁,使用 defer 在函数结束时进行释放
alloc.mu.Lock()
defer alloc.mu.Unlock()
// 第一次的时候 base 和 end 都为 0,所以会执行 generate()
// 否则直接返回 alloc.base++
if alloc.base == alloc.end {
end, err := alloc.generate()
if err != nil {
return 0, err
}
alloc.end = end
alloc.base = alloc.end - allocStep
}
alloc.base++
return alloc.base, nil
}
func (alloc *AllocatorImpl) generate() (uint64, error) {
// 获取要给 XXPath 分配 ID 的 key
key := alloc.getAllocIDPath()
// 从 etcd 中读取 key 所对应的值
value, err := etcdutil.GetValue(alloc.client, key)
if err != nil {
return 0, err
}
var (
cmp clientv3.Cmp
end uint64
)
if value == nil {
// create the key
cmp = clientv3.Compare(clientv3.CreateRevision(key), "=", 0)
} else {
// update the key
end, err = typeutil.BytesToUint64(value)
if err != nil {
return 0, err
}
cmp = clientv3.Compare(clientv3.Value(key), "=", string(value))
}
// 如果以前不存在,则 end 被赋值为 1000(分配的步长),否则,就是原有的值+步长
end += allocStep
// 将 uint64 转为 bytes
value = typeutil.Uint64ToBytes(end)
// 从 etcd 获取一个事务,然后将值提交到 etcd 中
txn := kv.NewSlowLogTxn(alloc.client)
leaderPath := path.Join(alloc.rootPath, "leader")
t := txn.If(append([]clientv3.Cmp{cmp}, clientv3.Compare(clientv3.Value(leaderPath), "=", alloc.member))...)
resp, err := t.Then(clientv3.OpPut(key, string(value))).Commit()
if err != nil {
return 0, err
}
if !resp.Succeeded {
return 0, errors.New("generate id failed, we may not leader")
}
log.Info("idAllocator allocates a new id", zap.Uint64("alloc-id", end))
idGauge.WithLabelValues("idalloc").Set(float64(end))
return end, nil
}
func (alloc *AllocatorImpl) getAllocIDPath() string {
return path.Join(alloc.rootPath, "alloc_id")
}
|
etcd 中事务是原子执行的,只支持 if … then … else … 这种表达,能实现一些有意思的场景。
其他的一些 Alloc 调用
pd/server/cluster.go#AllocPeer()pd/server/cluster_worker.go#handleAskSplit()pd/server/grpc_service.go#AllocID()pd/table/namespace_classifier.go#CreateNamespace()
主要的调用逻辑代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
newRegionID, err := c.s.idAllocator.Alloc()
...
peerIDs := make([]uint64, len(request.Region.Peers))
for i := 0; i < len(peerIDs); i++ {
if peerIDs[i], err = c.s.idAllocator.Alloc(); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
}
|
相关统计
pd 在启动时,调用 metricutil.Push(&cfg.Metric) 即可开启 prometheus 的上报客户端,默认情况下:每 15 秒上报一次。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
// prometheusPushClient pushs metrics to Prometheus Pushgateway.
func prometheusPushClient(job, addr string, interval time.Duration) {
for {
err := push.FromGatherer(
job, push.HostnameGroupingKey(),
addr,
prometheus.DefaultGatherer,
)
if err != nil {
log.Error("could not push metrics to Prometheus Pushgateway", zap.Error(err))
}
time.Sleep(interval)
}
}
// Push metircs in background.
func Push(cfg *MetricConfig) {
if cfg.PushInterval.Duration == zeroDuration || len(cfg.PushAddress) == 0 {
log.Info("disable Prometheus push client")
return
}
log.Info("start Prometheus push client")
interval := cfg.PushInterval.Duration
go prometheusPushClient(cfg.PushJob, cfg.PushAddress, interval)
}
|
每成功重新 generate() 一次的时候,就会上报一次 prometheus。
idGauge.WithLabelValues("idalloc").Set(float64(end))
高可用容灾
- 可以参考美团《Leaf 高可用容灾》
- 可以参见有赞《如何做一个靠谱的发号器》
参考资料
- TiDB 整体架构
- Placement Driver 功能介绍
- 介绍 PD Google Slides
- TiDB 中的 TSO
- 常见分布式全局唯一 ID 生成策略及算法的对比
- 阿里 P8 架构师谈:分布式系统全局唯一 ID 简介、特点、5 种生成方式
- 全局唯一 ID 在分布式系统中用来做什么用?
- etcd v3 客户端用法
- 如何做一个靠谱的发号器
- 高并发分布式系统唯一 ID 生成
- 微信序列号生成器架构设计及演变
- etcd 性能表现(官方)
附 TUG 华南区 Shopee 深圳第三期线下活动信息
https://www.huodongxing.com/event/3513772048600

活动的详细安排

后续 https://asktug.com 也会将活动实录整理好后放出来,有兴趣的小伙伴们可以关注。
茶歇驿站
一个可以让你停下来看一看,在茶歇之余给你帮助的小站,这里的内容主要是后端技术,个人管理,团队管理,以及其他个人杂想。


